Liquid chromatography analysis
Intraduction
Ion chromatography is a sub-type of high-performance liquid chromatography, also known as high-performance ion chromatography (HPIC). This is based on the equilibrium of ion exchange between ions in the sample/mobile phase and the oppositely charged counter ions to pair with that are fixed to the stationary phase. High end HPIC system are equipped with automatic eluent generation system which can generate the required potassium hydroxide or methanesulfonic acid eluent sloution automatically from a concentrated reservoir. HPIC coupled with electrical conductivity and DC ampere detectors is applied for the separation of hydrophilic anions, cations, amino acids and sugars.
Sample submission:
To ensure accuracy of experimental results, the samples submitted should meet the following requirements: at least 100~200 μL for body fluids (serum, plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, lymph, urine, saliva, etc.) , at least 5×106~1×107 for cells, 30~200 mg for animal tissue; 100 mg~1 g for plant tissue, and 1×107~1×108 for microbe.
Please provide detailed information about the target metabolites and related literature, including but not limited to the name of the target compound, CAS number, structural formula, literature or determination method from other sources.
Please provide the standard target compound with high purity. If you need BMSC’s assistance in procurement of the standard compounds, please wait patiently, as some compounds may have a long time of delivery.
Sample processing:
The samples such as blood, tissue, cell, and body fluid are extracted with an organic extraction solution (80%-100% methanol or acetonitrile). The metabolites are extracted by homogenization, ultrasonication, or shaking. After centrifuging, the supernatant can be directly analyzed (after dilution when needed) by mass spectrometry. The supernatant can also be concentrated or purified by solid phase extraction (SPE) before chromatography analysis.
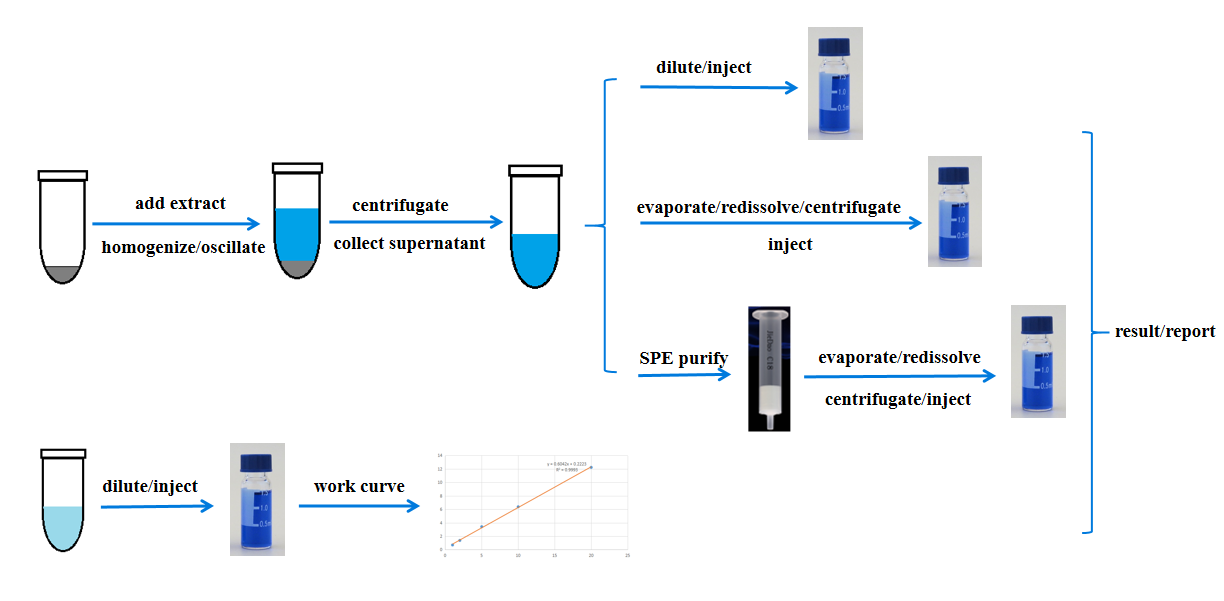
Result output:
The concentrations of target metabolites are quantified with internal standard or external standard methods with default quantitative data analysis software from the instrument vendor. The results will be sent by email. If you need the original raw data, please download from data storage server at HPC core facility.
© 2023 by Personal Life Coach. Proudly created with Wix.com ICP备案号:京ICP备18029179号



